FAQ
How to reach us?
- 💬 Join our Discord Community
- 📧 Email us at support@bytebase.com
- 🎫 Open GitHub Issue
- 🤠 Find us on @Bytebase
Supported languages
English, 简体中文, Español, 日本語
Certifications
SOC 2 Type II.
System requirements
Resources
Bytebase is a single Go binary and is lightweight.
CPU and RAM
| Usage | Bytebase | External PostgreSQL if used |
|---|---|---|
| 5 users and 5 instances | 1 CPU cores and 2 GB RAM | 1 CPU cores and 2 GB RAM |
| 20 users and 20 instances | 2 CPU cores and 4 GB RAM | 1 CPU cores and 2 GB RAM |
| 50 users and 50 instances | 4 CPU cores and 8 GB RAM | 2 CPU cores and 4 GB RAM |
| Above 250 users or 50 instances | 8 CPU cores and 16 GB RAM | 2 CPU cores and 4 GB RAM |
Storage
Bytebase stores the SQL statements. If your team submits large SQL statements frequently, then you need to reserve large disk space. A good starting point is to reserve 100 GB for where the Bytebase server runs. And if you use External PostgreSQL, then you need to make sure to reserve enough space there.
Docker
If you use Docker to deploy Bytebase, please use Docker version >= 20.10.24.
WebSocket
SQL Editor autocomplete requires enabling WebSocket in your gateway if present.
Does Bytebase retain your data
Bytebase does not retain any database row data.
Database credentials
In order to perform database operations on users' behalf, Bytebase needs users to provide the database credentials. By default, Bytebase stores the supplied credentials in the obfuscated format. For the Enterprise plan, you can instruct Bytebase to use the external secret manager.
Database schema (metadata)
Bytebase syncs and stores the database schema information. If you enable AI Assistant, Bytebase will also send the schema info to OpenAI or the configured endpoint.
Database data (row data)
When you query the database via Bytebase, Bytebase does not store the result data. Audit log only records the query.
If you enable Data Rollback, Bytebase will store the backup data in your own database instance.
Production Setup
See Production Setup.
Supported database and versions
See Supported Databases.
Supported version control systems (VCS) and providers
See Git Provider.
How to enable https
How to enable debug mode
Debug mode is a global setting and is only supposed to be used for troubleshooting.
Debug mode emits more detailed logs on the backend as well as returning more verbose logs to the frontend.
Enable --debug on startup
You can pass --debug when starting Bytebase.
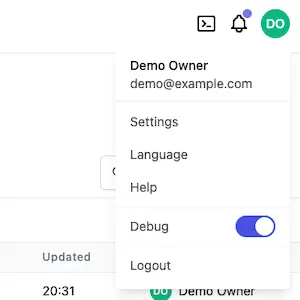
Toggle debug mode at runtime
If you are an OWNER or DBA, you can also toggle debug mode at runtime. The toggle is under the top-right profile dropdown
Does Bytebase support post action after applying a change to the database
You can configure project webhook to observe events.
Which data does Bytebase collect?
To make deployment air-gapped, you can disable the collection by passing --disable-metric on startup.
- Anonymous usage data.
- The registered email and name of the first member in the workspace.